code chunk
install.packages("maptools",
repos = "https://packagemanager.posit.co/cran/2023-10-13")Shubham Sinha
September 6, 2025
September 13, 2025
maptools is retired and its binary is removed from CRAN. However, we can download it from Posit Public Package Manager snapshots by using following code
Include
#| eval: falsein the code chunk to avoid maptools being downloaded and installed repetitively every time the Quarto document is rendered.
The code chunk below install and load following packages into R environment:
Data sets in this exercise are as follows:
CHILDCARE (Point Feature Data)
MP14_SUBZONE_WEB_PL (Polygon Feature Data)
CostalOutline (Polygon Feature Data)
We will use st_read() of sf package will be used to import these three geospatial data sets into R.
Since the childcare_sf simple feature data frame is in the WGS84 geodetic CRS, which is not ideal for geospatial analysis, the st_transform() function from the sf package is used to reproject the data to the SVY21 coordinate system during import.
Reading layer `ChildCareServices' from data source
`D:\ssinha8752\ISSS608-VAA\In-class_Ex\In-class_Ex02\data\ChildCareServices.geojson'
using driver `GeoJSON'
Simple feature collection with 1925 features and 2 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XYZ
Bounding box: xmin: 103.6878 ymin: 1.247759 xmax: 103.9897 ymax: 1.462134
z_range: zmin: 0 zmax: 0
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84Let’s verify the crs of the data frame to ensure we’re using EPSG 3414.
Coordinate Reference System:
User input: EPSG:3414
wkt:
PROJCRS["SVY21 / Singapore TM",
BASEGEOGCRS["SVY21",
DATUM["SVY21",
ELLIPSOID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433]],
ID["EPSG",4757]],
CONVERSION["Singapore Transverse Mercator",
METHOD["Transverse Mercator",
ID["EPSG",9807]],
PARAMETER["Latitude of natural origin",1.36666666666667,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8801]],
PARAMETER["Longitude of natural origin",103.833333333333,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8802]],
PARAMETER["Scale factor at natural origin",1,
SCALEUNIT["unity",1],
ID["EPSG",8805]],
PARAMETER["False easting",28001.642,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8806]],
PARAMETER["False northing",38744.572,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8807]]],
CS[Cartesian,2],
AXIS["northing (N)",north,
ORDER[1],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
AXIS["easting (E)",east,
ORDER[2],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
USAGE[
SCOPE["Cadastre, engineering survey, topographic mapping."],
AREA["Singapore - onshore and offshore."],
BBOX[1.13,103.59,1.47,104.07]],
ID["EPSG",3414]]Let’s load the Master Plan Planning data using st_read() function
Reading layer `MP14_SUBZONE_WEB_PL' from data source
`D:\ssinha8752\ISSS608-VAA\In-class_Ex\In-class_Ex02\data'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 323 features and 15 fields
Geometry type: MULTIPOLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 2667.538 ymin: 15748.72 xmax: 56396.44 ymax: 50256.33
Projected CRS: SVY21Let’s check coordinate system of this data frame
Coordinate Reference System:
User input: SVY21
wkt:
PROJCRS["SVY21",
BASEGEOGCRS["SVY21[WGS84]",
DATUM["World Geodetic System 1984",
ELLIPSOID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
ID["EPSG",6326]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,
ANGLEUNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]]],
CONVERSION["unnamed",
METHOD["Transverse Mercator",
ID["EPSG",9807]],
PARAMETER["Latitude of natural origin",1.36666666666667,
ANGLEUNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8801]],
PARAMETER["Longitude of natural origin",103.833333333333,
ANGLEUNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8802]],
PARAMETER["Scale factor at natural origin",1,
SCALEUNIT["unity",1],
ID["EPSG",8805]],
PARAMETER["False easting",28001.642,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8806]],
PARAMETER["False northing",38744.572,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8807]]],
CS[Cartesian,2],
AXIS["(E)",east,
ORDER[1],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1,
ID["EPSG",9001]]],
AXIS["(N)",north,
ORDER[2],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1,
ID["EPSG",9001]]]]mpsz_sf is also using EPSG 9001 instead of 3414 which is suitable for CRS SVY21. Let’s assign correct EPSG code using st_set_crs() then verify the output.
Warning: st_crs<- : replacing crs does not reproject data; use st_transform for
thatCoordinate Reference System:
User input: EPSG:3414
wkt:
PROJCRS["SVY21 / Singapore TM",
BASEGEOGCRS["SVY21",
DATUM["SVY21",
ELLIPSOID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433]],
ID["EPSG",4757]],
CONVERSION["Singapore Transverse Mercator",
METHOD["Transverse Mercator",
ID["EPSG",9807]],
PARAMETER["Latitude of natural origin",1.36666666666667,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8801]],
PARAMETER["Longitude of natural origin",103.833333333333,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8802]],
PARAMETER["Scale factor at natural origin",1,
SCALEUNIT["unity",1],
ID["EPSG",8805]],
PARAMETER["False easting",28001.642,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8806]],
PARAMETER["False northing",38744.572,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8807]]],
CS[Cartesian,2],
AXIS["northing (N)",north,
ORDER[1],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
AXIS["easting (E)",east,
ORDER[2],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
USAGE[
SCOPE["Cadastre, engineering survey, topographic mapping."],
AREA["Singapore - onshore and offshore."],
BBOX[1.13,103.59,1.47,104.07]],
ID["EPSG",3414]]st_union()is used to derive the coastal outline sf tibble data.frame
sg_sf will look similar to the figure below.
We can use as.ppp() of spatstat.geom package to derive an ppp object layer directly from a sf tibble data.frame.
Geometry set for 1925 features
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XYZ
Bounding box: xmin: 11810.03 ymin: 25596.33 xmax: 45404.24 ymax: 49300.88
z_range: zmin: 0 zmax: 0
Projected CRS: SVY21 / Singapore TM
First 5 geometries:POINT Z (40985.94 33848.38 0)POINT Z (28308.65 45530.47 0)POINT Z (17828.84 36607.36 0)POINT Z (25579.73 29221.89 0)POINT Z (38981.02 32483.41 0)Coordinate Reference System:
User input: EPSG:3414
wkt:
PROJCRS["SVY21 / Singapore TM",
BASEGEOGCRS["SVY21",
DATUM["SVY21",
ELLIPSOID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433]],
ID["EPSG",4757]],
CONVERSION["Singapore Transverse Mercator",
METHOD["Transverse Mercator",
ID["EPSG",9807]],
PARAMETER["Latitude of natural origin",1.36666666666667,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8801]],
PARAMETER["Longitude of natural origin",103.833333333333,
ANGLEUNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433],
ID["EPSG",8802]],
PARAMETER["Scale factor at natural origin",1,
SCALEUNIT["unity",1],
ID["EPSG",8805]],
PARAMETER["False easting",28001.642,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8806]],
PARAMETER["False northing",38744.572,
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1],
ID["EPSG",8807]]],
CS[Cartesian,2],
AXIS["northing (N)",north,
ORDER[1],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
AXIS["easting (E)",east,
ORDER[2],
LENGTHUNIT["metre",1]],
USAGE[
SCOPE["Cadastre, engineering survey, topographic mapping."],
AREA["Singapore - onshore and offshore."],
BBOX[1.13,103.59,1.47,104.07]],
ID["EPSG",3414]]Warning: data contain duplicated points
Let’s reveal the properties of the newly created ppp objects using summary().
Marked planar point pattern: 1925 points
Average intensity 2.461811e-06 points per square unit
*Pattern contains duplicated points*
Coordinates are given to 11 decimal places
marks are numeric, of type 'double'
Summary:
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
0 0 0 0 0 0
Window: polygonal boundary
80 separate polygons (35 holes)
vertices area relative.area
polygon 1 14650 6.97996e+08 8.93e-01
polygon 2 (hole) 3 -2.21090e+00 -2.83e-09
polygon 3 285 1.61128e+06 2.06e-03
polygon 4 (hole) 3 -2.05920e-03 -2.63e-12
polygon 5 (hole) 3 -8.83647e-03 -1.13e-11
polygon 6 668 5.40368e+07 6.91e-02
polygon 7 44 2.26577e+03 2.90e-06
polygon 8 27 1.50315e+04 1.92e-05
polygon 9 711 1.28815e+07 1.65e-02
polygon 10 (hole) 36 -4.01660e+04 -5.14e-05
polygon 11 (hole) 317 -5.11280e+04 -6.54e-05
polygon 12 (hole) 3 -3.41405e-01 -4.37e-10
polygon 13 (hole) 3 -2.89050e-05 -3.70e-14
polygon 14 77 3.29939e+05 4.22e-04
polygon 15 30 2.80002e+04 3.58e-05
polygon 16 (hole) 3 -2.83151e-01 -3.62e-10
polygon 17 71 8.18750e+03 1.05e-05
polygon 18 (hole) 3 -1.68316e-04 -2.15e-13
polygon 19 (hole) 36 -7.79904e+03 -9.97e-06
polygon 20 (hole) 4 -2.05611e-02 -2.63e-11
polygon 21 (hole) 3 -2.18000e-06 -2.79e-15
polygon 22 (hole) 3 -3.65501e-03 -4.67e-12
polygon 23 (hole) 3 -4.95057e-02 -6.33e-11
polygon 24 (hole) 3 -3.99521e-02 -5.11e-11
polygon 25 (hole) 3 -6.62377e-01 -8.47e-10
polygon 26 (hole) 3 -2.09065e-03 -2.67e-12
polygon 27 91 1.49663e+04 1.91e-05
polygon 28 (hole) 26 -1.25665e+03 -1.61e-06
polygon 29 (hole) 349 -1.21433e+03 -1.55e-06
polygon 30 (hole) 20 -4.39069e+00 -5.62e-09
polygon 31 (hole) 48 -1.38338e+02 -1.77e-07
polygon 32 (hole) 28 -1.99862e+01 -2.56e-08
polygon 33 40 1.38607e+04 1.77e-05
polygon 34 (hole) 40 -6.00381e+03 -7.68e-06
polygon 35 (hole) 7 -1.40545e-01 -1.80e-10
polygon 36 (hole) 12 -8.36709e+01 -1.07e-07
polygon 37 45 2.51218e+03 3.21e-06
polygon 38 142 3.22293e+03 4.12e-06
polygon 39 148 3.10395e+03 3.97e-06
polygon 40 75 1.73526e+04 2.22e-05
polygon 41 83 5.28920e+03 6.76e-06
polygon 42 211 4.70521e+05 6.02e-04
polygon 43 106 3.04104e+03 3.89e-06
polygon 44 266 1.50631e+06 1.93e-03
polygon 45 71 5.63061e+03 7.20e-06
polygon 46 10 1.99717e+02 2.55e-07
polygon 47 478 2.06120e+06 2.64e-03
polygon 48 155 2.67502e+05 3.42e-04
polygon 49 1027 1.27782e+06 1.63e-03
polygon 50 (hole) 3 -1.16959e-03 -1.50e-12
polygon 51 65 8.42861e+04 1.08e-04
polygon 52 47 3.82087e+04 4.89e-05
polygon 53 6 4.50259e+02 5.76e-07
polygon 54 132 9.53357e+04 1.22e-04
polygon 55 (hole) 3 -3.23310e-04 -4.13e-13
polygon 56 4 2.69313e+02 3.44e-07
polygon 57 (hole) 3 -1.46474e-03 -1.87e-12
polygon 58 1045 4.44510e+06 5.68e-03
polygon 59 22 6.74651e+03 8.63e-06
polygon 60 64 3.43149e+04 4.39e-05
polygon 61 (hole) 3 -1.98390e-03 -2.54e-12
polygon 62 (hole) 4 -1.13774e-02 -1.46e-11
polygon 63 14 5.86546e+03 7.50e-06
polygon 64 95 5.96187e+04 7.62e-05
polygon 65 (hole) 4 -1.86410e-02 -2.38e-11
polygon 66 (hole) 3 -5.12482e-03 -6.55e-12
polygon 67 (hole) 3 -1.96410e-03 -2.51e-12
polygon 68 (hole) 3 -5.55856e-03 -7.11e-12
polygon 69 234 2.08755e+06 2.67e-03
polygon 70 10 4.90942e+02 6.28e-07
polygon 71 234 4.72886e+05 6.05e-04
polygon 72 (hole) 13 -3.91907e+02 -5.01e-07
polygon 73 15 4.03300e+04 5.16e-05
polygon 74 227 1.10308e+06 1.41e-03
polygon 75 10 6.60195e+03 8.44e-06
polygon 76 19 3.09221e+04 3.95e-05
polygon 77 145 9.61782e+05 1.23e-03
polygon 78 30 4.28933e+03 5.49e-06
polygon 79 37 1.29481e+04 1.66e-05
polygon 80 4 9.47108e+01 1.21e-07
enclosing rectangle: [2667.54, 56396.44] x [15748.72, 50256.33] units
(53730 x 34510 units)
Window area = 781945000 square units
Fraction of frame area: 0.422We can use as.owin() of spatstat.geom package to create an owin object layer directly from a sf tibble data.frame.
Let’s reveal the properties of the newly created owin objects using summary().
Window: polygonal boundary
80 separate polygons (35 holes)
vertices area relative.area
polygon 1 14650 6.97996e+08 8.93e-01
polygon 2 (hole) 3 -2.21090e+00 -2.83e-09
polygon 3 285 1.61128e+06 2.06e-03
polygon 4 (hole) 3 -2.05920e-03 -2.63e-12
polygon 5 (hole) 3 -8.83647e-03 -1.13e-11
polygon 6 668 5.40368e+07 6.91e-02
polygon 7 44 2.26577e+03 2.90e-06
polygon 8 27 1.50315e+04 1.92e-05
polygon 9 711 1.28815e+07 1.65e-02
polygon 10 (hole) 36 -4.01660e+04 -5.14e-05
polygon 11 (hole) 317 -5.11280e+04 -6.54e-05
polygon 12 (hole) 3 -3.41405e-01 -4.37e-10
polygon 13 (hole) 3 -2.89050e-05 -3.70e-14
polygon 14 77 3.29939e+05 4.22e-04
polygon 15 30 2.80002e+04 3.58e-05
polygon 16 (hole) 3 -2.83151e-01 -3.62e-10
polygon 17 71 8.18750e+03 1.05e-05
polygon 18 (hole) 3 -1.68316e-04 -2.15e-13
polygon 19 (hole) 36 -7.79904e+03 -9.97e-06
polygon 20 (hole) 4 -2.05611e-02 -2.63e-11
polygon 21 (hole) 3 -2.18000e-06 -2.79e-15
polygon 22 (hole) 3 -3.65501e-03 -4.67e-12
polygon 23 (hole) 3 -4.95057e-02 -6.33e-11
polygon 24 (hole) 3 -3.99521e-02 -5.11e-11
polygon 25 (hole) 3 -6.62377e-01 -8.47e-10
polygon 26 (hole) 3 -2.09065e-03 -2.67e-12
polygon 27 91 1.49663e+04 1.91e-05
polygon 28 (hole) 26 -1.25665e+03 -1.61e-06
polygon 29 (hole) 349 -1.21433e+03 -1.55e-06
polygon 30 (hole) 20 -4.39069e+00 -5.62e-09
polygon 31 (hole) 48 -1.38338e+02 -1.77e-07
polygon 32 (hole) 28 -1.99862e+01 -2.56e-08
polygon 33 40 1.38607e+04 1.77e-05
polygon 34 (hole) 40 -6.00381e+03 -7.68e-06
polygon 35 (hole) 7 -1.40545e-01 -1.80e-10
polygon 36 (hole) 12 -8.36709e+01 -1.07e-07
polygon 37 45 2.51218e+03 3.21e-06
polygon 38 142 3.22293e+03 4.12e-06
polygon 39 148 3.10395e+03 3.97e-06
polygon 40 75 1.73526e+04 2.22e-05
polygon 41 83 5.28920e+03 6.76e-06
polygon 42 211 4.70521e+05 6.02e-04
polygon 43 106 3.04104e+03 3.89e-06
polygon 44 266 1.50631e+06 1.93e-03
polygon 45 71 5.63061e+03 7.20e-06
polygon 46 10 1.99717e+02 2.55e-07
polygon 47 478 2.06120e+06 2.64e-03
polygon 48 155 2.67502e+05 3.42e-04
polygon 49 1027 1.27782e+06 1.63e-03
polygon 50 (hole) 3 -1.16959e-03 -1.50e-12
polygon 51 65 8.42861e+04 1.08e-04
polygon 52 47 3.82087e+04 4.89e-05
polygon 53 6 4.50259e+02 5.76e-07
polygon 54 132 9.53357e+04 1.22e-04
polygon 55 (hole) 3 -3.23310e-04 -4.13e-13
polygon 56 4 2.69313e+02 3.44e-07
polygon 57 (hole) 3 -1.46474e-03 -1.87e-12
polygon 58 1045 4.44510e+06 5.68e-03
polygon 59 22 6.74651e+03 8.63e-06
polygon 60 64 3.43149e+04 4.39e-05
polygon 61 (hole) 3 -1.98390e-03 -2.54e-12
polygon 62 (hole) 4 -1.13774e-02 -1.46e-11
polygon 63 14 5.86546e+03 7.50e-06
polygon 64 95 5.96187e+04 7.62e-05
polygon 65 (hole) 4 -1.86410e-02 -2.38e-11
polygon 66 (hole) 3 -5.12482e-03 -6.55e-12
polygon 67 (hole) 3 -1.96410e-03 -2.51e-12
polygon 68 (hole) 3 -5.55856e-03 -7.11e-12
polygon 69 234 2.08755e+06 2.67e-03
polygon 70 10 4.90942e+02 6.28e-07
polygon 71 234 4.72886e+05 6.05e-04
polygon 72 (hole) 13 -3.91907e+02 -5.01e-07
polygon 73 15 4.03300e+04 5.16e-05
polygon 74 227 1.10308e+06 1.41e-03
polygon 75 10 6.60195e+03 8.44e-06
polygon 76 19 3.09221e+04 3.95e-05
polygon 77 145 9.61782e+05 1.23e-03
polygon 78 30 4.28933e+03 5.49e-06
polygon 79 37 1.29481e+04 1.66e-05
polygon 80 4 9.47108e+01 1.21e-07
enclosing rectangle: [2667.54, 56396.44] x [15748.72, 50256.33] units
(53730 x 34510 units)
Window area = 781945000 square units
Fraction of frame area: 0.422Now we’ll create an ppp object by combining childcare_ppp and sg_owin then plot the output.
Before performing Kernel Density Estimation, we need to re-scale the unit of measurement from meter to kilometer.
There are two ways to convert KDE output into grid object
library(spatstat.geom)
library(raster)
library(sp)
# Set background color
par(bg = '#E4D5C9')
# Convert spatstat image to raster
r <- raster(kde_childcareSG_adaptive)
# Convert raster to SpatialGridDataFrame
gridded_kde_childcareSG_ad <- as(r, "SpatialGridDataFrame")
# Plot using spplot
spplot(gridded_kde_childcareSG_ad)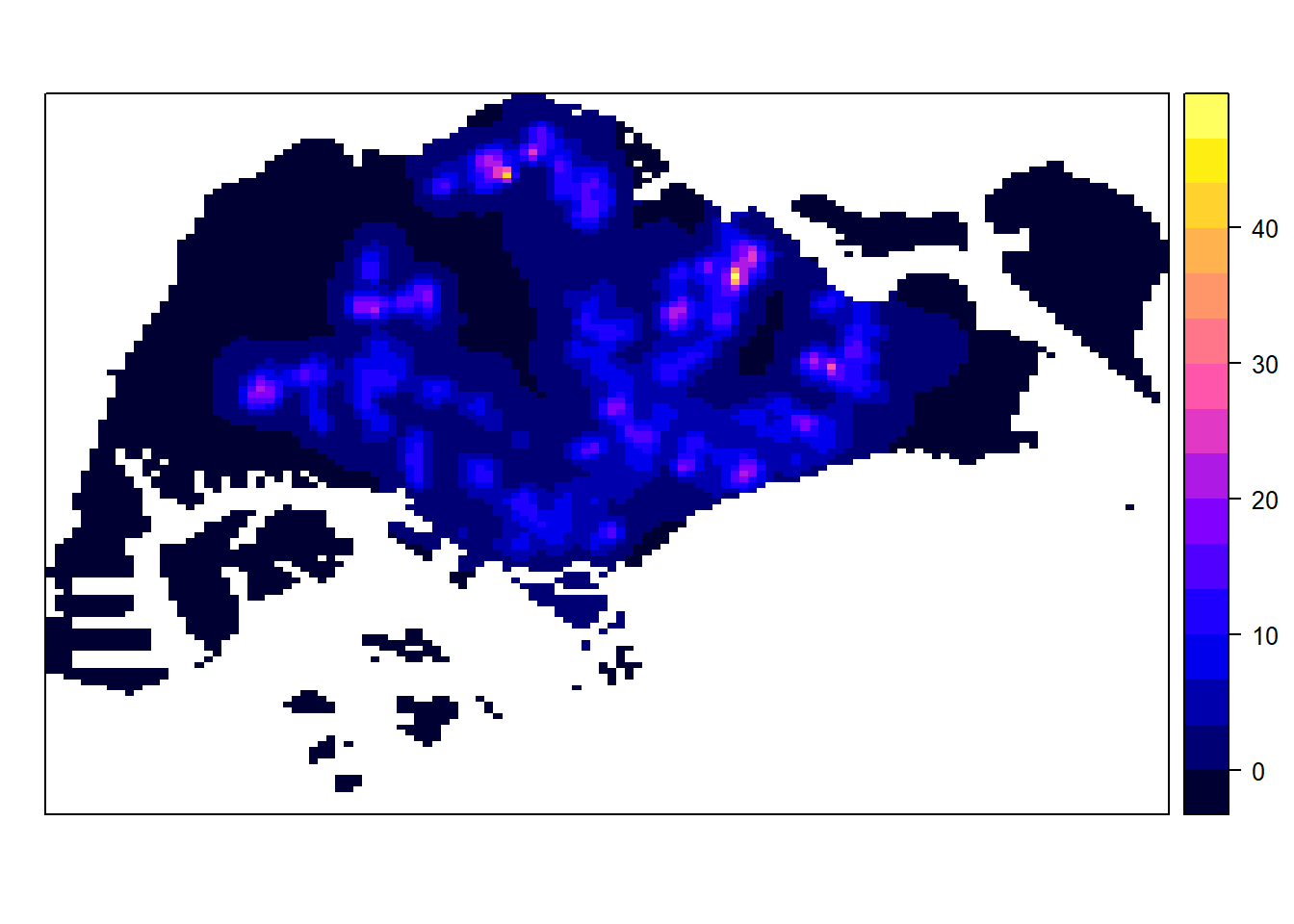
tmapWe can plot the output raster by using tmap functions.
── tmap v3 code detected ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────[v3->v4] `tm_tm_raster()`: migrate the argument(s) related to the scale of the
visual variable `col` namely 'palette' (rename to 'values') to col.scale =
tm_scale(<HERE>).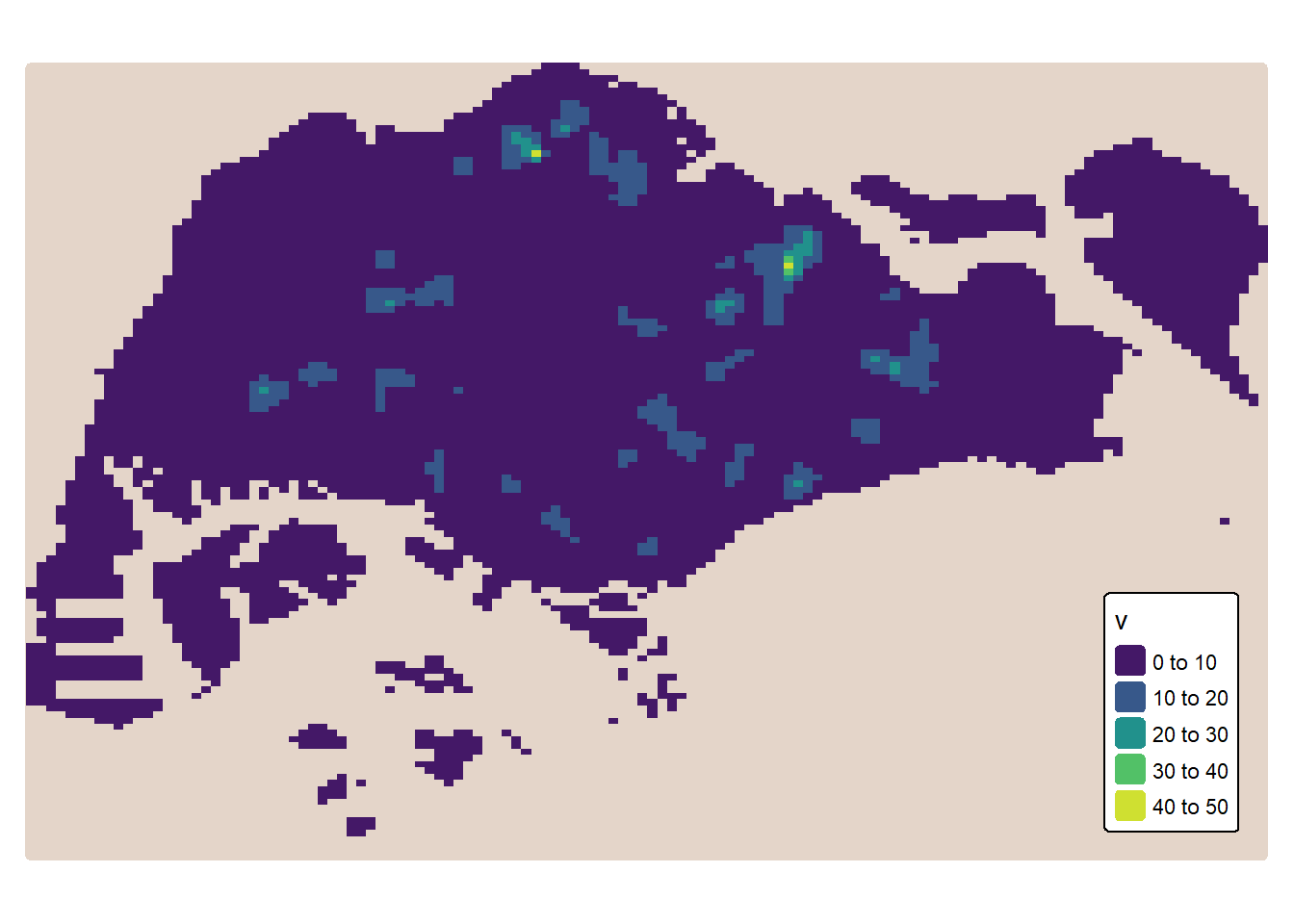
In order to ensure reproducibility, it is important to include the code chunk below before using spatstat functions involve Monte Carlo simulation
Kam, T. S. In-class Exercise 2: Spatial Point Patterns Analysis: spatstat methods. ISSS626 Geospatial Analytics and Applications.